From RAG to GraphRAG: A Practical Example of Connected, Predictable AI Reasoning
Understanding the theory of GraphRAG is one thing, but seeing it solve a real-world problem is another. In this tutorial, we’ll look at a Fleet Management scenario and Patient-Medication-Side-Effect relationship to demonstrate causal link discovery and that demonstrates exactly why standard RAG hits a wall where GraphRAG thrives.
The Fleet Management Scenario: The Disjointed Dispatcher
Imagine you are managing a logistics company. You have Drivers, Vehicles, Maintenance Logs, and Service Zones. Your data is stored across various PDFs, manuals, and databases.
Why Standard RAG Fails
Traditional RAG relies on Vector Similarity. When you ask this question:
- It finds chunks about "Weather Risks".
- It finds chunks about "Safety Inspection Schedules".
- It finds chunks about "Driver Assignments".
But because these facts live in different documents (or different parts of the same document), the vector search doesn't know Sarah (Driver) is in Zone A (Risk) and driving Truck 42 (Overdue). It retrieves the pieces but can't connect them.
The Knowledge Graph Solution
GraphRAG transforms these isolated chunks into a connected web of facts. Here is how that same data looks in a Knowledge Graph:
graph TD
Driver[Sarah Connor] -- ASSIGNED_TO --> Vehicle[Truck 42]
Vehicle -- OVERDUE --> Inspection[Safety Audit]
Driver -- CURRENTLY_IN --> Zone[Zone Alpha]
Zone -- HAS_STATUS --> Risk[Severe Weather Warning]
Risk -- IMPACTS --> Zone
The "Multi-hop" Traversal
With this structure, the AI doesn't "guess" based on similarity. It traverses:
- Start at
Severe Weather Warning→ FindZone Alpha - Find all
DriversinZone Alpha→ IdentifiedSarah Connor - Follow
Sarah ConnortoTruck 42 - Check if
Truck 42has anOVERDUErelationship to anInspection
Code Comparison: Search vs. Traversal
Vector Search (Approximate)
# Python (Pseudocode)
results = vector_db.search(
"weather risks and safety inspections",
top_k=5
)
# LLM tries to "hallucinate" the connections
# between unrelated text chunks.Cypher Query (Deterministic)
// Neo4j Cypher
MATCH (d:Driver)-[:IN]->(z:Zone {risk: 'High'})
MATCH (d)-[:DRIVES]->(v:Vehicle)
MATCH (v)-[:HAS_STATUS]->(s:Status {type: 'Overdue'})
RETURN d.name, v.id, z.nameBehind the Scenes: The Prompt Difference
The real magic of GraphRAG happens in the context window. Let’s look at exactly what the LLM sees in each mode when we ask: "Find drivers in high-risk zones with unsafe vehicles."
Disconnected Fragments
DATA:
- Driver Sarah Connor has 10 years experience.
- Truck42 missed its safety inspection.
- Severe Weather Alert for Zone Alpha.
QUERY: Find drivers in high-risk zones...The LLM has no evidence that Sarah is in Zone Alpha or driving Truck42.
Structured Traversal
DATA (Traversed Path):
Sarah Connor -> DRIVES -> Truck42
Sarah Connor -> CURRENT_IN -> Zone Alpha
WeatherWarning -> AFFECTS -> Zone Alpha
Truck42 -> STATUS -> Maintenance Overdue
QUERY: Find drivers in high-risk zones...The LLM now has 100% deterministic proof of the connection.
The Result: Precision vs. Uncertainty
When you run the demo, the difference in the final answer is striking:
Automated Verification
A secondary benefit of GraphRAG is Observability and Explainability. Because the system traverses a graph, it can automatically generate a visualization of its reasoning path.
The included Python demo script generates a graph_visualization.png file (using NetworkX and
Matplotlib) every time it runs, allowing users to verify that the "Multi-hop" logic is correctly
mapping to reality.
Try it Yourself: Hands-on Demo
Here is a practical couple of Python demonstration scripts that lets you run this exact scenario on your own machine.
Step 1:Install dependencies
websockets>=12.0
google-auth>=2.23.0
certifi>=2023.7.22
requests>=2.31.0
google-cloud-storage>=2.13.0
fastapi>=0.104.0
uvicorn>=0.23.2
google-generativeai>=0.3.0
networkx>=3.0
matplotlib>=3.8.0
pip install -r requirements.txtStep 2: Run the graphrag_demo.py script
graphrag_demo.pypython3 graphrag_demo.pyThe script will output a side-by-side comparison of how a standard RAG system (Vector Similarity) retrieves disconnected facts versus how a GraphRAG system (Traversals) identifies the exact "Multi-hop" path to the answer.
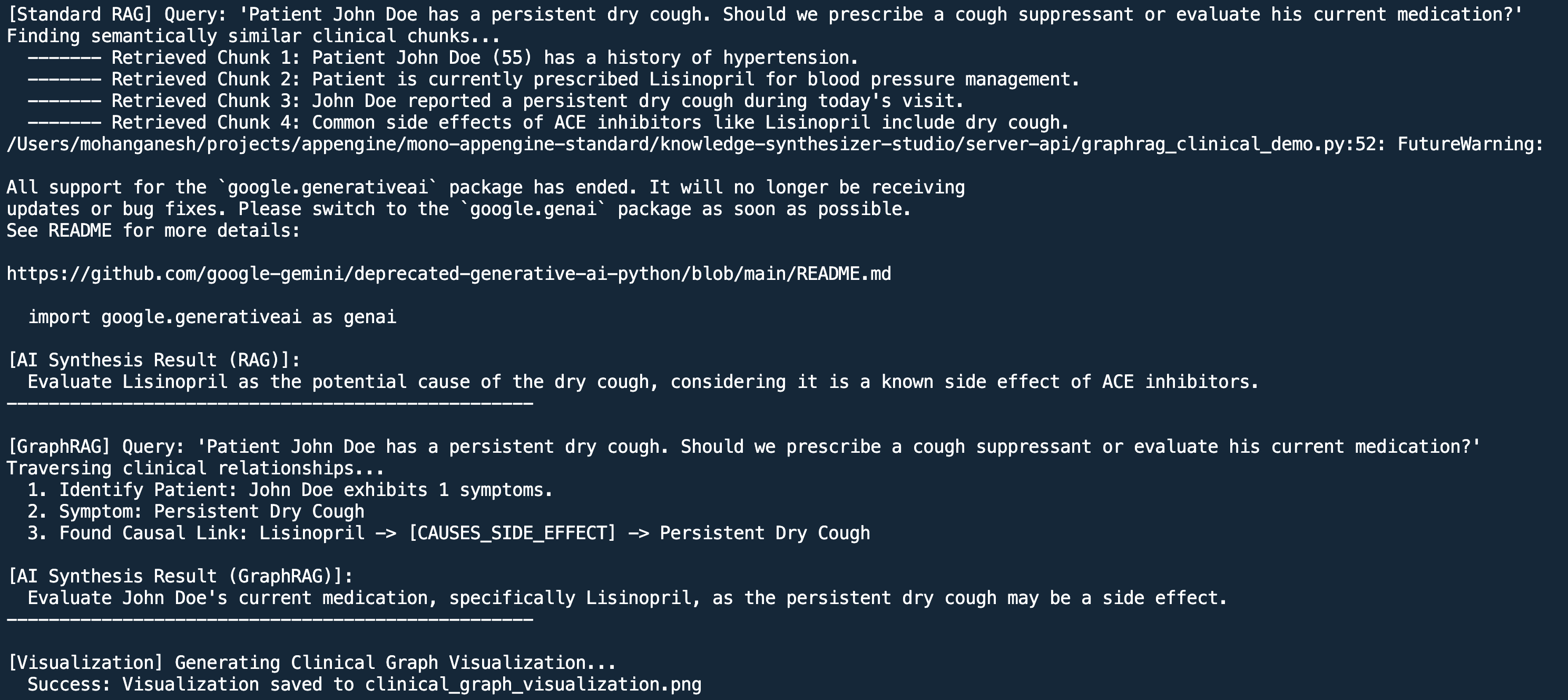
Clinical Case Study: Causal Link Discovery
Beyond fleet management, GraphRAG is transformative in Healthcare. In clinical settings, document fragmentation often hides critical causal links between medications and symptoms.
graph LR
Patient[John Doe] -- TAKES_MED --> Med[Lisinopril]
Med -- TREATS --> Cond[Hypertension]
Med -- CAUSES_SIDE_EFFECT --> Symptom[Persistent Cough]
Patient -- EXHIBITS --> Symptom
In this case, a standard RAG search might find a doctor's note about the cough and a separate
prescription
for Lisinopril, but fail to link them. GraphRAG immediately sees the
CAUSES_SIDE_EFFECT edge, allowing the AI to recommend a medication review rather than just
treating the symptom.
Run the Clinical Demo
graphrag_clinical_demo.pypython3 graphrag_clinical_demo.pyThis script demonstrates how traversal identifies that the cough is a side effect of the patient's existing medication, rather than a new condition requiring a new prescription.
Key Takeaways
- Precision over Recall: GraphRAG gives you the exact path, not just a list of related documents.
- Explainable AI: You can see exactly which nodes were traversed to reach the answer.
- Data Integrity: Centralizing entities prevents "Sarah Connor" from being treated differently than "S. Connor" across different documents.
Want to see the underlying data model?
Check out our guide on Foundational vs Decorative
Schema to learn how to design these graphs.
