RAG vs GraphRAG — How Knowledge Graphs Make AI More Reliable
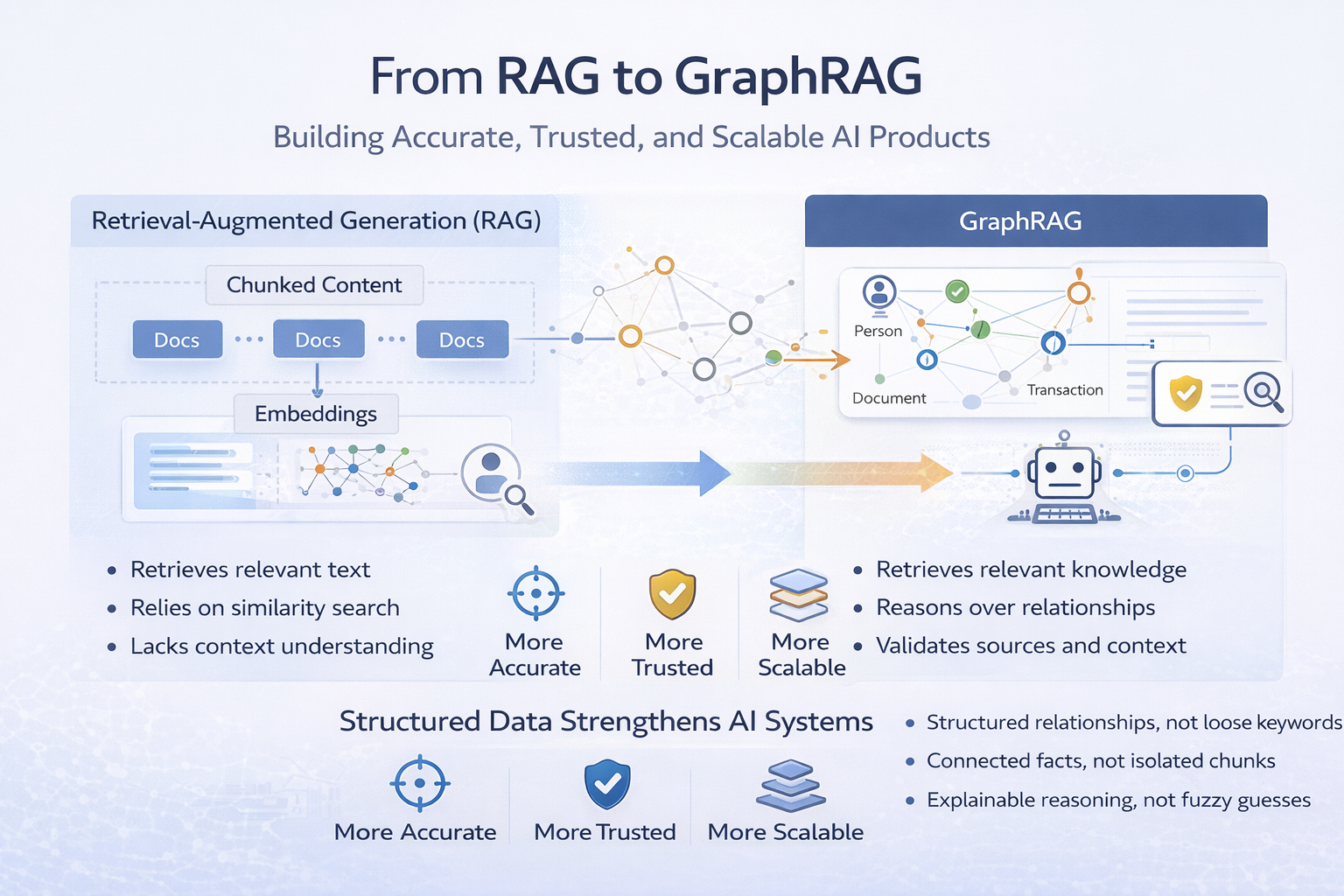
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) solved an important problem: LLMs should not rely only on their training data. But as enterprises began adopting RAG at scale, a new problem emerged: The model retrieves relevant text—but not reliable meaning. Standard RAG has a "fragmentation" problem; it retrieves document chunks based on similarity, often missing the global context and structured connections that define enterprise knowledge. GraphRAG naturally evolves this architecture by building a Knowledge Graph that enables:- Multi-hop Reasoning: Connecting dots across disparate documents that standard RAG would miss.
- Global Synthesis: Understanding thematic structures across an entire dataset, not just local pages.
- Deterministic Accuracy: Replacing "proximity-based guessing" with "edge-based traversal."
Traditional RAG: Powerful, But Shallow
In a standard RAG system:
- Content is chunked
- Chunks are embedded
- Similarity search retrieves “relevant” text
The LLM generates an answer
This works well for:
- FAQs
- documentation lookup
- unstructured knowledge bases
But it struggles in enterprise environments because similarity ≠ correctness.
The model retrieves what sounds related, not what is:
- authoritative
- contextually valid
- safe to combine
Why GraphRAG Changes perhaps improve the approach
GraphRAG introduces explicit relationships into the retrieval process. Instead of asking:Identity → Graph Nodes
Traditional RAG
Often relies on text chunks where entities are ambiguous strings.
GraphRAG
- Every node represents a real entity
- Not a document
- Not a paragraph
JSON-LD ensures:
- a
Person,Account, orPatientis uniquely identifiable - nodes are reused, not duplicated
This prevents one of the most common RAG failures: entity fragmentation.
The "@id" Handshake
This is where the theory becomes infrastructure. The JSON-LD @id isn't just
metadata—it
is the Primary Key (IRI) that binds your Graph Database to your Knowledge
Model.
Input: JSON-LD (Source)
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Patient",
"@id": "https://garvik.dev/patient/bh-123",
"name": "Sarah Connor"
}Query: Cypher (Neo4j) / GQL (Spanner)
MATCH (p:Patient)
WHERE p.iri = 'https://garvik.dev/patient/bh-123'
RETURN p.history, p.medicationsUsing iri
(Internationalized
Resource Identifier) as the key signals alignment with Semantic Web standards, ensuring global
uniqueness across federated graphs.
Authority → Trusted Subgraphs
Traditional RAG
Treats retrieved chunks as equal if they are semantically similar to the query.
GraphRAG
GraphRAG allows the system to prefer:
- certain nodes
- certain edges
- certain paths
Structured authority metadata lets the AI reason:
This dramatically reduces hallucinations.
Relationships → Traversal, Not Guessing
Traditional RAG
Classic RAG guesses relationships by proximity in text.
GraphRAG
GraphRAG traverses them explicitly:
- Person → Account → Transaction
- Member → Claim → Provider → Coverage
JSON-LD encodes these relationships upfront, so AI doesn’t invent them.
Context → Time-Aware Reasoning
Traditional RAG
Often retrieves outdated or irrelevant chunks if they match keywords.
GraphRAG
Graph edges can carry:
- effective dates
- states
- conditions
GraphRAG retrieves only the valid subgraph for the current context.
This avoids answers that are:
- outdated
- legally invalid
- operationally wrong
Provenance → Explainable Paths
Traditional RAG
Hard to explain why a specific chunk was chosen or synthesized.
GraphRAG
One of GraphRAG’s most underrated strengths is explainability. With structured provenance:
- the AI can show how it reached an answer
- which nodes and edges were used
- which sources were authoritative
This is critical for:
- audits
- regulators
- internal trust
Trust Boundaries → Safe Graph Cuts
Traditional RAG
Difficult to enforce complex access rules on unstructured text chunks.
GraphRAG
GraphRAG allows you to define:
- which subgraphs can be traversed together
- which edges are restricted
JSON-LD can encode privacy and access rules so AI agents:
- do not cross compliance boundaries
- do not combine disallowed data
This turns governance into architecture, not policy slides.
Intent → Focused Retrieval
Traditional RAG
Retrieves "everything related," often including irrelevant presentation text.
GraphRAG
Retrieves:
- only the parts of the graph relevant to the user’s intent
Foundational schemas define meaning.
Decorative layers define presentation.
This separation keeps AI systems precise and trustworthy.
A Mental Model Worth Keeping
Structured data defines what truth means.
Without foundational structure, GraphRAG is just a graph of guesses.
With it, AI systems become:
- composable
- auditable
- enterprise-grade
Why This Makes AI More Reliable and Accurate
GraphRAG systems built on structured data:
- hallucinate less
- reason more consistently
- adapt better to change
explain their outputs
respect enterprise constraints
Most importantly:
In regulated or high-stakes environments, this is the difference between a demo and production.
Closing Insight
LLMs are incredible at language. They are terrible at authority. GraphRAG + structured data doesn’t make AI smarter — It makes AI responsible. And that’s the real leap from experimentation to production.
Lets see this in action?
Lets see this in action with a practical example.
